Creating a ZIP File and push to D365 Using REST API in Logic Apps
I will receive a CSV file, which I need to convert into a ZIP file. This ZIP file will then be pushed to D365.
To create the ZIP file, I have developed an Azure Function. The input file for the function will be the CSV file, and within the code, I will fetch the manifest files from the blob storage.
Creating a ZIP File Using Azure Function
1. I have a CSV file that needs to be converted into a ZIP file, which will include two manifest XML files.
2. The CSV file is picked from the input.
3. The manifest XML files are stored in blob storage. Within the code, I connect to the blob storage and retrieve the XML files.
4. These three files (the CSV and two XML files) are added to the ZIP file, which is then returned by the function.
Click Here to create Azure Function:
Code:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs;
using Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs.Extensions.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Blob;
using System.IO.Compression;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Auth;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage;
namespace Test.test.CreateZip
{
public static class CreateZipFile
{
[FunctionName("CreateZipFile")]
public static async Task<IActionResult> Run(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, "get", "post", Route = null)] HttpRequest req,
ILogger log)
{
try
{
log.LogInformation("CreateZipFile function triggered");
if (req.Body != null)
{
string fileName = req.Query["FileName"];
string processName = req.Query["ProcessName"];
CloudBlobClient cloudBlobClient;
CloudBlobContainer cloudBlobContainer;
CloudStorageAccount cloudStorageAccount;
string blobFolder = "";
// Connecting to azure blob
cloudStorageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("BlobConnectionString"));
cloudBlobClient = cloudStorageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
cloudBlobContainer = cloudBlobClient.GetContainerReference(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("BlobContainerName"));
switch (processName)
{
case "Process1": blobFolder = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("Prcoess1Folder"); break;
case "Prcoess2": blobFolder = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("Prcoess2Folder"); break;
case "Prcoess3": blobFolder = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("Prcoess3Folder"); break;
}
CloudBlobDirectory cloudBlobDirectory = cloudBlobContainer.GetDirectoryReference(blobFolder);
if (cloudBlobDirectory == null)
{
log.LogError("An error occurred : Blob is not connected. Check the Environment Variables");
return new BadRequestObjectResult("Blob is not connected. Check the Environment Variables");
}
CloudBlockBlob Manifestblob = cloudBlobDirectory.GetBlockBlobReference("Manifest.xml");
CloudBlockBlob PackageHeaderblob = cloudBlobDirectory.GetBlockBlobReference("PackageHeader.xml");
using (var zipStream = new MemoryStream())
{
// Adding files to zip stream
using (var archive = new ZipArchive(zipStream, ZipArchiveMode.Create, true))
{
await AddToZipFile(archive, fileName, null, req.Body);
await AddToZipFile(archive, "Manifest.xml", Manifestblob);
await AddToZipFile(archive, "PackageHeader.xml", PackageHeaderblob);
}
zipStream.Position = 0;
//Adding zip stream to response
req.HttpContext.Response.ContentType = "application/zip";
req.HttpContext.Response.Headers["Content-Disposition"] = $"attachment; filename={processName + ".zip"}";
await zipStream.CopyToAsync(req.HttpContext.Response.Body);
}
return new OkObjectResult(req.HttpContext.Response.Body);
}
else
{
log.LogError("An error occurred : File is mandatory");
return new BadRequestObjectResult("File is mandatory");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
log.LogError(ex, "An error occurred");
return new BadRequestObjectResult(ex.ToString());
}
}
public static async Task<MemoryStream> downloadAsync(CloudBlockBlob blob)
{
//Downoad the file from blob
using (var stream = new MemoryStream())
{
await blob.DownloadToStreamAsync(stream);
return stream;
}
}
public static async Task AddToZipFile(ZipArchive archive, string fileName, CloudBlockBlob blob, Stream inputStream = null)
{
var zipFile = archive.CreateEntry(fileName, CompressionLevel.Optimal);
// Add the file to zip stream
using (var entryStream = zipFile.Open())
{
if (blob != null)
{
var result = await downloadAsync(blob);
using (var fileToCompressStream = new MemoryStream(result.ToArray()))
{
fileToCompressStream.CopyTo(entryStream);
}
}
else
{
await inputStream.CopyToAsync(entryStream);
}
}
}
}
}
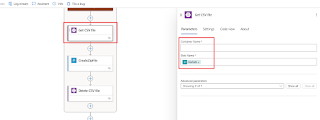
Process Workflow
1. Fetch the CSV file from blob storage and pass it to the Azure Function.
2. After the ZIP file is created, delete the original CSV file.
3. Generate an D365 authentication token.
4. Call the GetAzureWriteUrl API to retrieve a temporary blob URL.
URL: ('D365URL')/data/DataManagementDefinitionGroups/Microsoft.Dynamics.DataEntities.GetAzureWriteUrl
Headers:
{
"Authorization": "Bearer @{body('Generate_D365_Token')?['access_token']}"
}Body:
{
"uniqueFileName": "@{outputs('File_Name')?[triggerBody()?['ProcessName']]?['ImportProject']}_DMFPackage"
}
Get the temporary blob url from previous step.
json(body('Get_Azure_Write_URL')?['value'])
5. Upload the ZIP file to the temporary blob using the URL.
Headers:
{
"x-ms-blob-type": "BlockBlob"
}
6. Call the ImportFromPackage API to push the ZIP file to D365.
URL:
('D365URL')}/data/DataManagementDefinitionGroups/Microsoft.Dynamics.DataEntities.ImportFromPackage
Headers:
{
"Authorization": "Bearer @{body('Generate_D365_Token')?['access_token']}"
}body:
{
"packageUrl": "@{outputs('Fetch_blob_url')?['BlobUrl']}",
"definitionGroupId": @{outputs('File_Name')?[triggerBody()?['ProcessName']]?['ImportProject']},
"executionId": "",
"execute": true,
"overwrite": true,
"legalEntityId": @{triggerBody()?['Company']}
}
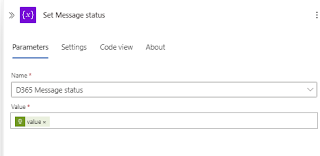
7. Add a 1-minute delay after calling the until function.
for until I have used the below expression.
or(equals(variables('D365 Message status'), 'Succeeded'),
equals(variables('D365 Message status'), 'PartiallySucceeded'),
equals(variables('D365 Message status'), 'Failed'),
equals(variables('D365 Message status'), 'Canceled'))8. Use the ExecutionSummary URL to check the import status.
URL:
('D365URL')}/data/DataManagementDefinitionGroups/Microsoft.Dynamics.DataEntities.GetExecutionSummaryStatusbody:
{
"executionId": "@{body('Push_file_to_D365')?['value']}"
}
9. Assign the status retrieved from the execution summary to the D365 message status variable.
10. If the status is not "Succeeded," send an email notification.
Response:
- CSV file is fetched from Blob.
- Function app return the zip file.
- 1st time the execution status is Executing
- 2nd time the execution status is Success.

Keep Daxing!!









































.png)